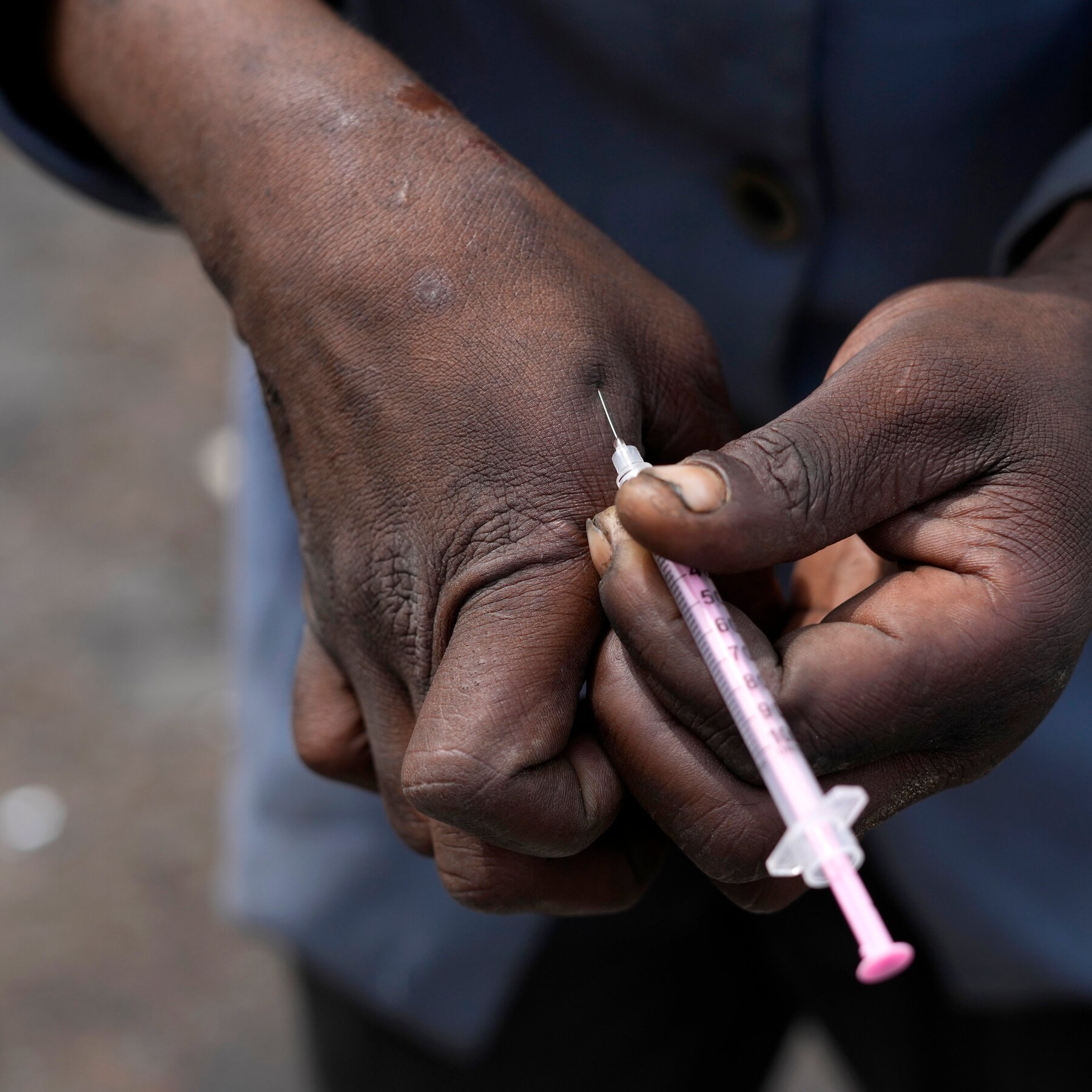
‘Bluetoothing’: Blood-Sharing Drug Trend Fuels Alarming Global H.I.V. Surge
‘Bluetoothing’: Blood-Sharing Drug Trend Fuels Alarming Global H.I.V. Surge
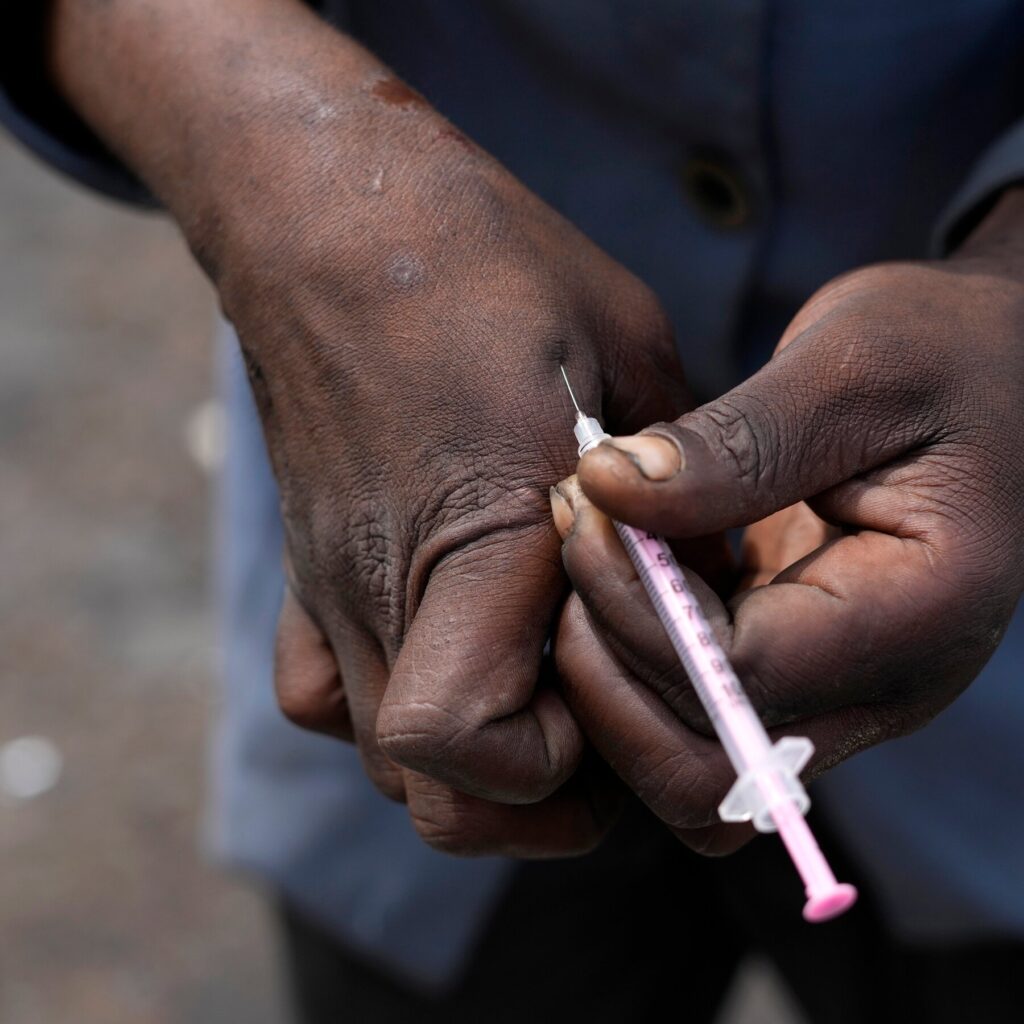

The practice, in which users inject the blood of already intoxicated individuals, has fueled one of the fastest-growing H.I.V. epidemics in the Pacific and grown widespread in South Africa.
Read the full article on NY Times World
Truth Analysis
Analysis Summary:
The article discusses a concerning trend called 'bluetoothing' and its alleged link to HIV outbreaks. While the existence of 'bluetoothing' and its association with drug use and HIV spread are supported by some sources, the claim of a global HIV surge directly fueled by this practice and its widespread presence in South Africa requires further verification. The article exhibits moderate bias through potentially exaggerated claims and selective reporting.
Detailed Analysis:
- Claim: The practice involves injecting the blood of already intoxicated individuals.
- Verification Source #2: Confirms 'bluetoothing' involves intravenous drug use and sharing blood.
- Verification Source #4: Confirms 'bluetoothing' involves intravenous drug use and sharing blood.
- Verification Source #3: Describes a similar practice where blood is withdrawn after drug use and injected into another person.
- Assessment: Supported
- Claim: This practice has fueled one of the fastest-growing H.I.V. epidemics in the Pacific.
- Verification Source #1: Reports on an HIV outbreak in Fiji linked to meth use and needle-sharing.
- Verification Source #5: Reports on a surge in HIV and AIDS cases in Fiji, fueled by methamphetamine use.
- Assessment: Supported, specifically in the context of Fiji and potentially other Pacific regions.
- Claim: The practice has grown widespread in South Africa.
- Assessment: Unverified. None of the provided sources mention South Africa.
- Claim: The practice is called 'bluetoothing'.
- Verification Source #2: Identifies the practice of sharing blood as 'bluetoothing'.
- Verification Source #4: Identifies the practice of sharing blood as 'bluetoothing'.
- Assessment: Supported
Supporting Evidence/Contradictions:
- Source 1: "...alarming needle-sharing trends accelerate the spread of the virus..."
- Source 5: "Fiji has asked the United Nations for help with a surge in HIV and AIDS cases, fuelled by the country's spiralling methamphetamine trade."
- The claim about South Africa is not supported by any of the provided sources.